Employee feedback is the secret ingredient that can transform your workplace from average to exceptional. As a business owner or manager, your goal is to create an environment where employees feel valued, understood, and motivated to perform at their best.
But here’s the thing — providing meaningful feedback isn’t always easy. Finding the right words, choosing the appropriate time, and delivering your message effectively requires skill and practice.
That’s why I’ve put together this comprehensive guide to employee feedback, complete with 25 different types and 50 practical employee feedback examples you can start using today.
Table of Contents:
- What is Employee Feedback?
- Why is Employee Feedback Important?
- How to Give and Get Employee Feedback
- How to Collect Employee Feedback
- Common Employee Survey Types
- 25 Types of Employee Feedback with Examples
- Following Up on Employee Feedback Effectively
- FAQs About Employee Feedback
What is Employee Feedback?
Employee feedback is a two-way communication process that includes both feedback given TO employees and feedback FROM employees.
It encompasses constructive comments, praise, evaluations, and insights shared between managers, employees, and colleagues regarding performance, workplace satisfaction, and organizational improvements.
Employee feedback serves multiple purposes:
Feedback TO Employees: Helps employees understand their performance, strengths, and areas for improvement. This includes performance reviews, coaching conversations, and recognition.
Feedback FROM Employees: Provides organizations with insights into employee satisfaction, workplace culture, management effectiveness, and suggestions for improvement.
Feedback can flow through various channels:
- Formal evaluations and performance reviews
- Employee satisfaction surveys
- Informal conversations and check-ins
- Peer assessments and 360-degree reviews
- Anonymous suggestion systems
- Exit interviews
The goal is to create a culture of continuous improvement where employees feel valued and heard, while also ensuring they have the guidance needed to excel in their roles.
Effective feedback balances positive reinforcement with constructive criticism, delivered through clear communication to support both individual growth and organizational success.
Why is Employee Feedback Important?
The impact of meaningful feedback on workplace engagement is undeniable. According to Gallup research, 80% of employees who report having received meaningful feedback in the past week are fully engaged.
That’s a powerful statistic that demonstrates just how crucial feedback is to your organization’s success!
Here are several reasons why employee feedback matters:
Facilitates Professional Growth
Feedback provides employees with insights into their performance, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement. This helps them enhance their skills and capabilities, contributing to their career advancement.
Creates a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Regular feedback promotes accountability and motivation among employees. When people know what’s expected of them and how they’re performing against those expectations, they’re more likely to take ownership of their work.
Strengthens Communication and Trust
Transparent feedback demonstrates a commitment to employee success and well-being. When managers take the time to provide thoughtful feedback, it shows they care about their team members’ development.
Boosts Engagement and Productivity
Recognizing employees’ contributions reinforces positive behaviors and motivates them to continue performing well.
By offering regular and meaningful feedback, you create a supportive and high-performing work environment that benefits both individuals and the organization as a whole.
How to Give and Get Employee Feedback
Delivering Constructive Feedback
Providing negative feedback is never easy, but it’s essential for growth. Here’s a seven-step approach to make it more effective:
- Choose the Right Time and Place: Find a private setting where the employee feels comfortable and respected.
- Be Specific and Objective: Focus on observable actions rather than subjective judgments, providing concrete examples.
- Offer Constructive Criticism: Address the behavior or performance issue, not the person, and suggest actionable steps for improvement.
- Use “I” Statements: Say “I noticed that project deadlines have been missed” rather than “You’re always late with your work.”
- Encourage Dialogue: Create an open environment where the employee can share their perspective and ask questions.
- Focus on Solutions: Collaborate with the employee to develop an improvement plan with clear expectations and goals.
- Follow Up: Schedule a meeting to review progress and provide ongoing support and encouragement.
Collecting Employee Feedback
To gain valuable insights from your team, consider these methods:
- Regular Surveys: Conduct periodic anonymous surveys to gather feedback on various aspects of the workplace.
- Open-Door Policy: Create an environment where employees feel comfortable approaching managers with their feedback and concerns.
- Anonymous Feedback Channels: Provide ways for employees to submit feedback confidentially, such as suggestion boxes or online forms.
- Performance Reviews: Use two-way feedback during reviews, allowing employees to share their perspectives on their performance and goals.
- Team Meetings: Integrate feedback sessions into regular meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and goals.
- Recognition Programs: Implement systems that encourage peers and managers to provide positive feedback for exceptional contributions.
Improving Satisfaction with the Feedback Process
Managers can enhance employee satisfaction with feedback by:
- Creating a safe environment for open communication
- Ensuring feedback sessions are constructive and supportive
- Approaching feedback with empathy
- Focusing on solutions and development opportunities
- Tailoring feedback to individual goals
- Providing concrete examples
- Establishing clear action items
- Being willing to listen and adjust
How to Collect Employee Feedback
The easiest way to collect employee feedback is through surveys. If you’re using WordPress, UserFeedback is the best plugin for gathering honest feedback from your team members quickly and efficiently.
This powerful tool makes it simple to create professional surveys without any coding knowledge, allowing you to focus on what matters most—understanding your employees’ experiences and improving your workplace culture.
UserFeedback stands out as the ideal solution for employee feedback collection because it offers:
- Unlimited surveys and responses without restrictions
- Pre-built templates designed for employee feedback
- Custom branding options to match your company’s style
- Conditional logic for adaptive questionnaires that change based on responses
- Anonymous feedback options to encourage honest responses
- Integration with Google Analytics for detailed reporting and insights
- Easy-to-use interface that requires no coding skills
The anonymous feedback feature is particularly important for employee surveys, as it encourages honest responses about sensitive topics like management effectiveness or workplace culture.
The conditional logic capability allows you to dive deeper into specific issues automatically, giving you richer insights without overwhelming employees with irrelevant questions.
Beyond surveys, there are other methods to consider for collecting employee feedback.
Regular one-on-one meetings create opportunities for personal conversations where employees might share concerns they wouldn’t express in a group setting.
An open-door policy encourages spontaneous feedback, while team meetings can be used to gather input on specific projects or processes.
Anonymous suggestion boxes, whether physical or digital, provide another outlet for employees who prefer not to identify themselves when sharing feedback.
Exit interviews are also valuable for understanding why employees leave and what could have been done differently to retain them.
Common Employee Survey Types
When it comes to gathering employee feedback, different types of surveys serve different purposes. Here are the most effective survey types you can implement in your organization:
Employee Satisfaction Surveys
These surveys measure how content employees are with their jobs, work environment, and overall experience. These surveys typically ask about compensation, benefits, work-life balance, and job fulfillment.
They’re perfect for identifying areas where your company excels and where improvements are needed.
Check out: 20 Customer Satisfaction Survey Examples & Templates to Use
Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) Surveys
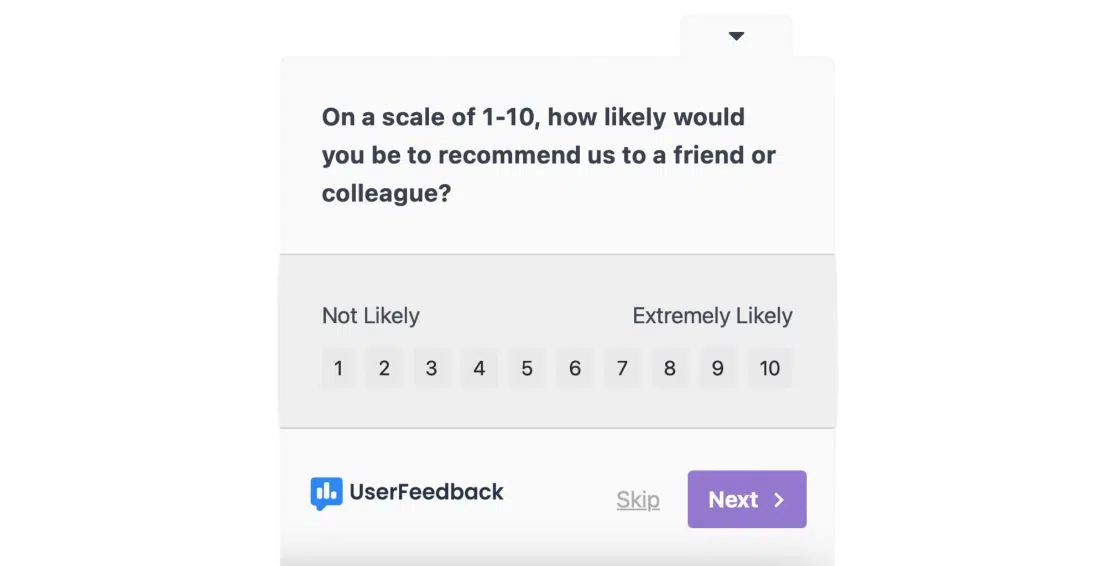
NPS surveys use a simple question: “How likely are you to recommend our company as a great place to work?” This provides a quick snapshot of employee loyalty and can help predict turnover rates.
Scores above 30 are generally considered good, while anything above 50 is excellent.
Read our full guide: How to Calculate NPS Score (Net Promotor Score) + Examples
Exit Interview Surveys
These capture valuable insights from departing employees about their experience and reasons for leaving. These surveys often reveal issues that current employees might not feel comfortable discussing, making them incredibly valuable for retention strategies.
Pulse Surveys
Pulse surveys are short, frequent surveys that track employee sentiment over time. Instead of waiting for annual reviews, pulse surveys help you spot trends and address issues quickly. They typically contain 5-10 questions and can be sent weekly or monthly.
360-Degree Feedback Surveys
These gather input from an employee’s manager, peers, and direct reports to provide a well-rounded view of their performance. These are particularly useful for leadership development and identifying blind spots.
Onboarding Surveys
Onboarding surveys collect feedback from new hires about their first few weeks or months on the job. This helps you refine your onboarding process and ensure new employees feel welcome and prepared.
Read our guide on: How to Make a Good Survey: 13 Practical Tips
25 Types of Employee Feedback with Examples
1. Positive feedback
Recognizing and praising an employee’s achievements, contributions, or positive behaviors.
Example 1: “Great job on completing the project ahead of schedule! Your dedication and hard work are truly commendable.”
Example 2: “Thank you for always going above and beyond to assist your colleagues. Your helpfulness is invaluable to the team.”
2. Constructive feedback
Providing feedback aimed at improving performance or correcting behavior in a supportive manner.
Example 1: “Your attention to detail is excellent, but I noticed a few areas in your presentation where you could improve clarity.”
Example 2: “Your communication skills are strong, but I think you could benefit from being more assertive in team meetings to ensure your ideas are heard.”
3. Performance feedback
Assessing an employee’s performance based on predefined goals, targets, or job responsibilities.
Example 1: “You consistently meet or exceed sales targets, demonstrating exceptional performance in driving revenue.”
Example 2: “Your ability to meet project deadlines and deliver high-quality work has significantly contributed to the success of our team.”
4. Developmental feedback
Offering feedback intended to help an employee grow, develop new skills, or advance in their career.
Example 1: “I see potential for you to further develop your leadership skills. Taking on a mentorship role for newer team members could help you grow in this area.”
Example 2: “Improving your time management skills could help you handle multiple projects more effectively. Consider using time-tracking tools or adopting prioritization techniques.”
5. Behavioral feedback
Addressing specific behaviors exhibited by an employee, whether positive or negative.
Example 1: “Your proactive approach to problem-solving has been instrumental in resolving issues before they escalate. Keep up the excellent work.”
Example 2: “I’ve noticed that you tend to interrupt others during meetings. Being more mindful of giving everyone a chance to speak will help foster better collaboration.”
6. Continuous feedback
Providing ongoing feedback on an employee’s performance, rather than waiting for formal reviews.
Example 1: “I wanted to provide some feedback on your recent project presentation. While your content was strong, I noticed that you spoke very quickly, making it challenging for the audience to follow. Maybe try to slow down your pace next time.”
Example 2: “Thank you for your quick response to the customer’s inquiry yesterday. Your timely assistance demonstrates your commitment to providing excellent customer service.”
7. Formal feedback
Scheduled feedback sessions or performance evaluations conducted at regular intervals, such as quarterly or annually.
Example 1: “During your quarterly performance review, we discussed areas where you excel, such as your strong analytical skills. We also identified opportunities for improvement, such as time management, which we’ll work on together in the coming months.”
Example 2: “Your annual performance evaluation highlighted your consistent contributions to the team’s success, including your ability to adapt to changing priorities and deliver results under pressure.”
8. Informal feedback
Spontaneous, day-to-day feedback given in casual conversations or interactions.
Example 1: “I wanted to let you know that your initiative in proposing new ideas during our team meetings is appreciated. Your creativity often sparks valuable discussions.”
Example 2: “Thanks for your help with the project yesterday. Your attention to detail ensured that everything ran smoothly.”
9. 360-degree feedback
Gathering feedback from multiple sources, including peers, managers, subordinates, and sometimes external stakeholders.
Example 1: “Your peers have highlighted your strong collaboration skills and ability to work well within a team.”
Example 2: “Your direct reports appreciate your supportive leadership style and willingness to listen to their concerns.”
10. Specific feedback
Providing detailed feedback on a particular aspect of performance or behavior.
Example 1: “Your presentation skills have improved significantly since our last training session. Your use of visuals and storytelling techniques made the content engaging and memorable.”
Example 2: “Your attention to detail in reviewing documents ensures that errors are caught early in the process, preventing delays.”
11. General feedback
Offering broad feedback that covers overall performance or behavior without focusing on specific details.
Example 1: “Overall, your performance has been consistently strong, and your positive attitude has a positive impact on the team dynamic.”
Example 2: “You consistently demonstrate professionalism and reliability in your work, which contributes to the overall success of the team.”
12. Timely feedback
Giving feedback promptly after an event or situation occurs, rather than waiting.
Example 1: “Thank you for stepping up and taking on additional responsibilities during our busiest period. Your flexibility and willingness to help out were greatly appreciated.”
Example 2: “I noticed that you handled the customer complaint with professionalism and empathy. Your quick response helped resolve the issue and maintain customer satisfaction.”
13. Goal-oriented feedback
Aligning feedback with an employee’s goals, objectives, or developmental plans.
Example 1: “Your progress towards achieving your quarterly sales targets has been impressive. Let’s discuss strategies to maintain this momentum and surpass our goals.”
Example 2: “You have made significant progress in improving your time management skills, which aligns with your goal of becoming more efficient in your work.”
14. Skill-based feedback
Providing feedback on specific skills or competencies relevant to the employee’s role.
Example 1: “Your technical skills in data analysis are exceptional, and your ability to interpret complex data sets sets you apart from your peers.”
Example 2: “Your proficiency in coding has improved significantly since you started taking online courses. Your dedication to skill development is commendable.”
15. Recognition feedback
Acknowledging and appreciating an employee’s efforts, accomplishments, or contributions.
Example 1: “Congratulations on receiving the Employee of the Month award! Your consistent dedication and positive attitude make you a valuable asset to the team.”
Example 2: “I wanted to acknowledge the outstanding customer feedback we received about your exceptional service. Your commitment to exceeding customer expectations is commendable.”
16. Corrective feedback
Addressing performance or behavior issues that need improvement.
Example 1: “I noticed that there were several errors in your report. Let’s review them together and discuss strategies to prevent similar mistakes in the future.”
Example 2: “Your tardiness has been impacting team meetings. Let’s work together to find a solution to ensure you can arrive on time consistently.”
17. Appreciative feedback
Expressing gratitude or appreciation for an employee’s efforts, attitude, or support.
Example 1: “Thank you for always being willing to lend a helping hand to your colleagues. Your willingness to support others does not go unnoticed.”
Example 2: “Your positive attitude and enthusiasm for your work are contagious and contribute to a positive work environment for everyone.”
18. Peer feedback
Feedback provided by colleagues or teammates rather than by a supervisor or manager.
Example 1: “I appreciate your collaborative approach to problem-solving. Your willingness to listen to different perspectives and work together as a team is commendable.”
Example 2: “Your attention to detail in reviewing project documents ensures that errors are caught early, saving time and preventing rework for the team.”
19. Managerial feedback
Feedback given by a supervisor or manager regarding an employee’s performance, behavior, or development.
Example 1: “Your leadership skills have had a positive impact on the team. Your ability to motivate and inspire others to achieve their goals is commendable.”
Example 2: “Your proactive approach to addressing customer concerns demonstrates your commitment to providing excellent service. Your efforts are appreciated by both the team and our customers.”
20. Self-assessment feedback
Encouraging employees to evaluate their own performance and providing feedback based on their self-assessment.
Example 1: “In your self-assessment, you identified communication skills as an area for improvement. Let’s discuss strategies to help you develop these skills further.”
Example 2: “You mentioned in your self-assessment that you struggle with time management. Let’s work together to identify time-saving techniques and prioritize tasks effectively.”
21. Situational feedback
Tailoring feedback to specific situations, projects, or tasks.
Example 1: “During the client presentation, your ability to answer questions confidently and articulate key points effectively was impressive.”
Example 2: “In the recent team meeting, I noticed that you actively contributed to the discussion and provided valuable insights.”
22. Long-term feedback
Discussing trends or patterns observed over an extended period, such as progress over several months or years.
Example 1: “Over the past year, your consistent dedication to your work and willingness to take on new challenges have been evident. Your contributions have been instrumental in the team’s success.”
Example 2: “Since joining the company, your growth and development have been remarkable. Your commitment to learning and improvement has positioned you as a valuable asset to the team.”
23. Performance improvement feedback
Offering feedback aimed at helping an employee overcome performance challenges or barriers.
Example 1: “Your recent sales numbers have been below expectations. Let’s work together to identify areas for improvement and develop a plan to help you achieve your targets.”
Example 2: “I’ve noticed that you’ve been struggling with meeting project deadlines. Let’s discuss strategies to improve time management and prioritize tasks effectively.”
24. Objective feedback
Providing feedback based on measurable, observable facts rather than subjective opinions.
Example 1: “Your ability to meet project deadlines consistently is evident from the project metrics, which show that you have completed all tasks on time.”
Example 2: “Customer feedback surveys consistently rate your service as excellent, highlighting your professionalism and commitment to customer satisfaction.”
25. Cultural fit feedback
Assessing how well an employee’s values, attitudes, and behaviors align with the organization’s culture and values.
Example 1: “Your ability to collaborate effectively with colleagues from different departments demonstrates your alignment with our company’s collaborative culture.”
Example 2: “Your enthusiasm for volunteering for company events and initiatives reflects your commitment to our company values of community engagement and social responsibility.”
Following Up on Employee Feedback Effectively
Following up is one of the most crucial aspects of the feedback process, ensuring that employees feel heard and valued. After gathering feedback, managers should acknowledge receipt and outline any actions or changes being considered.
A follow-up doesn’t have to be immediate, but regular updates keep employees informed and engaged.
When managers take steps to address feedback, employees are more likely to share future insights, knowing their input directly shapes company culture.
Here are some effective follow-up strategies:
- Schedule a follow-up meeting: Set a specific date to discuss progress and any challenges that have arisen.
- Document the feedback and action plan: Keep a record of the feedback provided and the agreed-upon steps for improvement.
- Provide resources and support: Offer training, mentoring, or other resources to help the employee implement changes.
- Recognize progress: Acknowledge and celebrate improvements, no matter how small.
- Adjust expectations if necessary: Be flexible and willing to modify goals or timelines based on the employee’s progress and circumstances.
And that’s it!
I hope you liked this comprehensive guide and list of employee feedback examples. Be sure to also read our guide, Employee Feedback Survey Questions That Actually Work.
Haven’t tried UserFeedback yet? What are you waiting for?
And don’t forget to follow us on X and Facebook to learn more about collecting user feedback online.
FAQs About Employee Feedback
How often should I give employee feedback?
While formal feedback might occur during scheduled performance reviews, effective managers provide informal feedback regularly. According to Gallup, employees who receive feedback weekly are 3.6 times more likely to be engaged than those who receive it annually. Aim for a mix of formal and informal feedback, with quick check-ins happening at least once a week.
What’s the difference between constructive feedback and criticism?
Constructive feedback focuses on improvement and growth, providing specific examples and actionable suggestions. It addresses behaviors rather than personal traits. Criticism, on the other hand, often feels judgmental, lacks specific guidance, and can come across as an attack on the person rather than their performance.
How do I give feedback to difficult employees?
When giving feedback to difficult employees, focus on specific behaviors rather than personality traits. Use clear, direct language and provide concrete examples. Maintain a calm, professional tone, and focus on finding solutions together. Set clear expectations for improvement and follow up consistently.
Should feedback always be given in private?
Positive feedback can be given in public or private, depending on the employee’s preference and company culture. However, constructive or corrective feedback should always be delivered privately to maintain the employee’s dignity and create a safe space for open discussion.
How can I encourage employees to give feedback to their managers?
Create a culture where feedback flows in all directions by modeling openness to feedback yourself. Implement anonymous feedback tools, regular check-ins, and surveys. Recognize and act on employee feedback to show that their input is valued and makes a difference.